Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing: A Modern Approach to Data Processing
In today’s digital landscape, data processing plays a crucial role in everything from smart devices to large-scale enterprise systems. As the need for faster, more efficient computing grows, two technologies—edge computing and cloud computing—have become central to how data is managed, processed, and stored. While both approaches have their distinct advantages, understanding their differences is key to selecting the right solution for specific needs.
What is Cloud Computing?
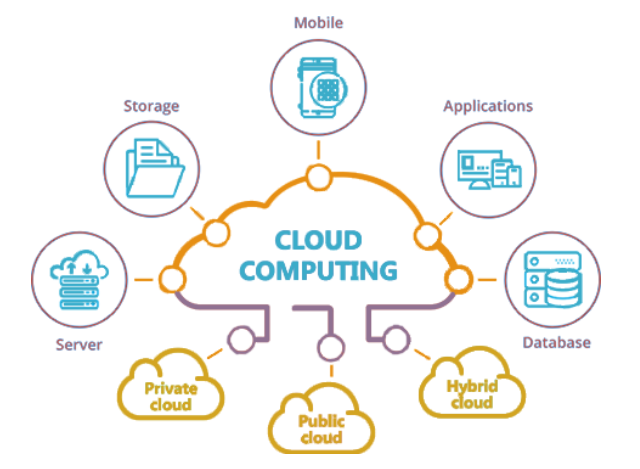
Cloud computing refers to the practice of using remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process data, rather than relying on local servers or personal devices. The concept of cloud architecture is built around centralized data centers where large volumes of data are processed and accessed over the internet.
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses and individuals access computing resources. Services like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud provide scalable solutions for storage, data processing, and computing power, allowing users to rent resources as needed. This has led to cost efficiency, flexibility, and easy scalability for organizations.
However, despite its many benefits, cloud computing can face challenges when it comes to latency and real-time data processing, particularly for applications that require immediate response times or operate in environments with limited internet connectivity.
What is Edge Computing?
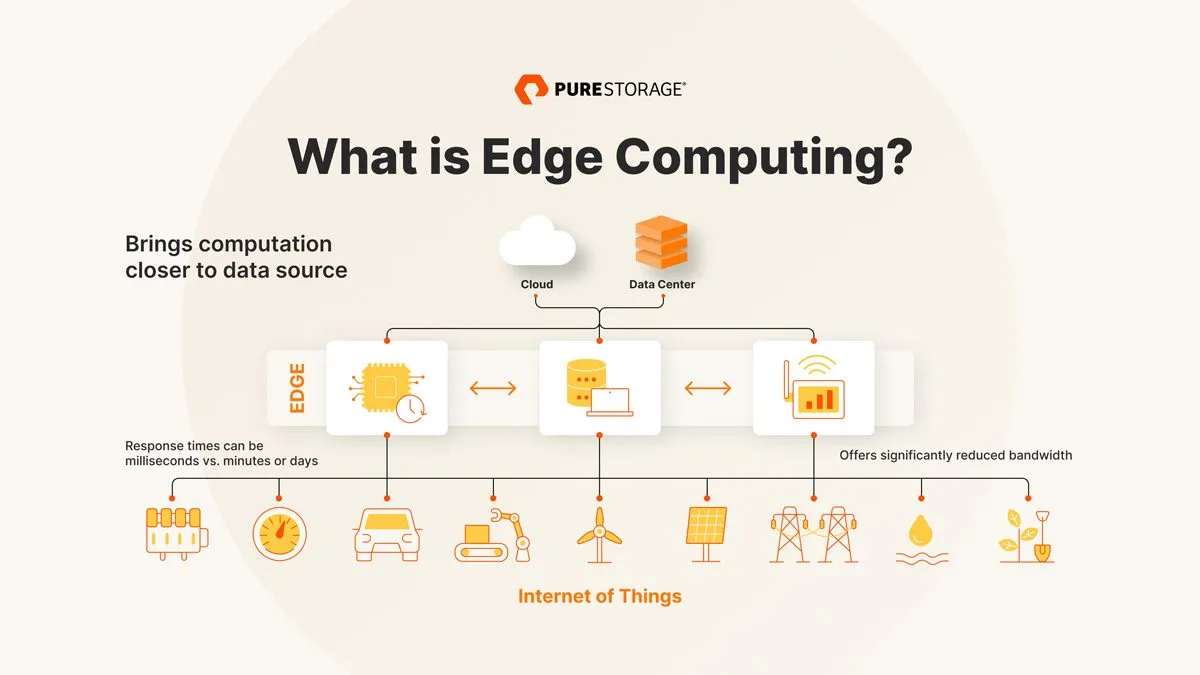
Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data closer to where it is generated, such as on local devices or at the “edge” of the network. Rather than sending all data to a centralized cloud for processing, edge computing handles data processing on-site or in proximity to the source. This approach is ideal for situations where data needs to be processed quickly, reducing the time it takes to send information back and forth to a cloud server.
Edge computing is particularly relevant for IoT (Internet of Things) edge devices. These devices—such as sensors, smart cameras, or autonomous vehicles—generate massive amounts of data. Processing this data directly at the source allows for latency reduction, which is essential for real-time applications like industrial automation, self-driving cars, and healthcare monitoring systems.
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing: Key Differences
1. Data Processing Location
-
Cloud computing relies on centralized servers, typically located in data centers across the world. Data is sent to these servers for processing, and then results are sent back to users or devices.
-
Edge computing, on the other hand, processes data at the source or nearby, in decentralized locations closer to the “edge” of the network.
2. Latency and Real-Time Processing
-
Cloud computing can face latency challenges due to the time it takes for data to travel to a centralized server, be processed, and then return to the user or device. This delay can be a problem for applications that need quickly processing.
-
Edge computing significantly reduces latency by performing processing on-site, enabling faster responses and real-time decision-making. This is particularly beneficial for applications like real-time video processing or autonomous systems.
3. Scalability and Flexibility
-
Cloud computing offers superior scalability because users can tap into virtually unlimited computing resources as needed. Cloud services allow businesses to easily scale up or down depending on their needs, making it suitable for large-scale applications and data storage.
-
Edge computing offers more localized, distributed solutions. While it may not have the same scalability as cloud systems, it is well-suited for handling specific, localized tasks with minimal delay.
4. Security and Privacy
-
Cloud computing is generally secure but raises concerns about data privacy, especially for sensitive information that travels over the internet. Although many cloud providers offer robust security protocols, the transmission of data across long distances can expose weaknesses.
-
Edge computing can offer more privacy and security benefits since data is processed locally and not transmitted across long distances. For industries like healthcare or finance, where data privacy is critical, edge computing offers a more secure solution.
Applications of Edge Computing and Cloud Computing
Both edge computing and cloud computing serve distinct roles across industries:
-
Edge computing is ideal for applications requiring real-time data processing, such as:
-
IoT edge devices like smart sensors, wearables, and connected vehicles.
-
Autonomous vehicles that need to process sensor data instantly for navigation and safety.
-
Manufacturing and automation where real-time analysis is critical for maintaining operational efficiency.
-
Cloud computing, with its scalable architecture, is best suited for:
-
Data storage and backup, allowing businesses to store large volumes of data securely.
-
Big data analytics, where vast datasets can be processed and analyzed to extract insights.
-
Web hosting and SaaS applications, where computing power can be accessed on-demand.
Hybrid Approach: The Future of Computing

While both edge and cloud computing have their own strengths, the future likely lies in a hybrid model, where both technologies work in unity. For example, edge computing can handle time-sensitive tasks, while cloud computing can manage bulk data storage and long-term analytics. Together, they create a comprehensive and efficient computing ecosystem that maximizes performance, reduces latency, and ensures scalability.
Conclusion

In summary, edge computing and cloud computing each have their distinct advantages depending on the use case. Edge computing is ideal for applications requiring real-time data processing with low latency, such as IoT and autonomous systems. On the other hand, cloud computing excels in providing scalable solutions for storage, large-scale data processing, and flexible resource management.
As the demand for faster and more efficient data processing continues to rise, organizations will need to carefully consider their specific requirements and choose between edge, cloud, or a combination of both to build the best solution for their needs.
Follow Us
Trending News
Newsletter
Aliqu justo et labore at eirmod justo sea erat diam dolor diam vero kasd